A Comprehensive Guide to Cold Room Classification
In a world where people’s material needs are increasing, it is vital that cold room maintain precise temperature control as a key part of the vital supply chain network that ensures the quality of demand. As the workhorse of controlled environment storage, cold rooms are far from a single solution. Their design, functionality and operating parameters vary widely depending on their specific needs. The classification of cold room varies greatly for different needs, and SDpanel has categorized them precisely.
Cold room classification based on temperature
Temperature is the defining characteristic of any cold room. The required storage temperature dictates the refrigeration system’s capacity, insulation levels, and overall design.
Positive temperature cold room
Positive temperature cold room, the temperature is usually between +2°C and +15°C, mainly for storing products that need to be cooled but not frozen. This is the most widely used category. It can store: fresh produce (fruit, vegetables, dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), beverages, certain medicines that need to be refrigerated, floral products, baked goods (dough retarders), cooked/prepared foods (short term).
Negative temperature cold room
We call the cold room with temperature below 0 degrees Negative Temperature Cold Room, which is divided into medium low temperature cold room, low temperature cold room, and ultra-low temperature cold room.
Medium low temperature cold room
This category includes freezers, which are among the most commonly used equipment and have temperature settings between 0°C and -18°C. They are designed to preserve seafood, meat and other specific commodities.
Low temperature cold room
The cold rooms in this category usually have a temperature range of -18°C to -30°C, or even lower to -35°C. It achieves long-term preservation of products by freezing, inhibiting microbial growth and enzyme activity. The main applications are: frozen foods (vegetables, fruits, meat, seafood, ready-to-eat foods, ice cream), frozen ingredients, certain biological samples, and some medicines. These devices play a key role in maintaining product quality and stability in cold chain logistics transportation.
Ultra-low temperature cold room
The temperature of these cold rooms is usually between (-40°C to -60°C), and optional lower temperatures can be set according to specific requirements. Special biopharmaceuticals, laboratory samples and chemicals need to be stored at ultra-low temperatures to maintain their unique properties. Ultra-low temperature cold rooms are mainly used to store highly sensitive biological and chemical materials that require extremely low temperatures for long-term stability. Main applications: vaccines (e.g., mRNA COVID-19 vaccines require -70°C), plasma, stem cells, tissues, enzymes, certain research reagents, forensic evidence. Specialized ultra-low temperature cold rooms are used for this purpose, although such products are not common on the market.
Cold rooms classification based on building type
How a cold room is built and integrated impacts its flexibility, cost, and installation time.
Prefabricated cold rooms
This refers to a modular, integrated cold room solution that is customized based on your needs and pre-assembled at the factory. Constructed using prefabricated PIR cold room panels, PUR cold room panels) assembled on site. Floor, wall and ceiling panels lock together. Typically contains pre-assembled doors and integrated refrigeration units. On-site installation simply follows blueprints and is assembled like building blocks, which greatly simplifies the installation process. Widely used in walk-in coolers/freezers in restaurants, supermarkets, distribution centers, breweries, pharmacies and small and medium-sized enterprises.
Built-In-Place cold rooms
A traditional building construction method whereby insulation materials (such as PIR cold storage panels) are applied on-site to structural walls, floors and ceilings within the existing building envelope. Built-In-Place Cold Rooms are highly customizable to fit irregular spaces or oversized volumes, and for oversized projects, material costs may be lower and seamlessly integrated with the building structure. They are mainly used in large industrial refrigerated warehouses, processing plant storage areas, and facilities that require special shapes or integration.
Cold room classification based on function
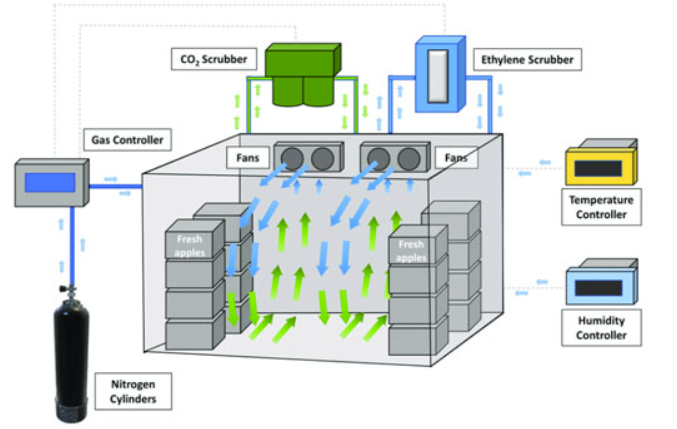
Controlled Atmosphere Storage (CA Storage)
CA Storage represents the most advanced method of preserving fruits and vegetables, by regulating the air composition in the storage environment, improving the preservation effect refrigeration technology. Air-conditioning preservation technology inhibits the respiratory process on the surface of fruits and vegetables by controlling the temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide, oxygen concentration and ethylene content, slowing down their metabolism and prolonging their freshness period.
Typically, gas-conditioning technology can extend the freshness period up to one times that of a traditional cold room. When the produce is removed from the air-conditioning technology, it slowly awakens from its dormant state and its freshness can be extended by about 20 days or more compared to other refrigeration methods.
IQF Tunnel Freezer
An IQF Tunnel Freezer is a continuous processing system designed for high throughput. Its core function is to expose individual product pieces to a high-velocity stream of extremely cold air in a controlled, linear tunnel environment. It consists of three main components: the product conveying system, the refrigeration circulation system and the ventilation system. As food items pass through the tunnel on flat trays, hanging or with the help of conveyor belts, they are cooled by refrigerants such as liquid nitrogen, forming a uniform layer of ice on the surface of the food. The ventilation equipment then continuously circulates the cold air inside to quickly reduce the temperature of the food to the desired ideal level.
It are mainly used in the food industry to quickly freeze a variety of products such as meat, poultry, fish, seafood, fruits, vegetables, semi-finished products, canned foods, bread and pastries.

Central cold room
The “Central cold room” represents the strategic core of large-scale temperature-controlled operations. Whether referring to the massive, multi-zone storage warehouse itself or the powerhouse refrigeration plant driving it, centralization delivers critical advantages in efficiency, control, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
The “central cold room” concept extends beyond large cold stores. Hospitals, universities, large hotels, food processing plants, and data centers often have central chiller plants producing chilled water that is then pumped to various Air Handling Units (AHUs) serving different building zones (including dedicated cold rooms, server rooms, and general comfort cooling).
Understanding the nuances of cold room classification – primarily by temperature, but also by construction, operation, and application – provides the essential framework for making informed decisions. We strongly recommend working with an experienced SDpanel to understand these classifications, translate requirements into technical specifications, and ensure that the selected solution will provide optimal performance, efficiency, and compliance for years to come.
